Visual Studio Code
Linux, C & Visual Studio Code
We’re going to be programming in the C programming language in this module. We’ll start learning some C in a couple of weeks time but we can do some preparation this week.
Linux
We will be using the Linux operating system. The PCs in this lab (and in CD105) are set up as dual boot machines. You can boot them in to Windows or Linux, specifically the Unbuntu variant of Linux. If you’ve already booted in to Linux congratulations, you’ve completed the first part of this task. If you are in Windows you’ll need to reboot the machine and choose the Ubuntu option during the start up. Remeber you’ll need to use your Linux/Computing account.
Linux is based on the Unix operating system. It is available for free from https://ubuntu.com/. Installing Ubuntu and setting it up can be a bit tricky/fiddly and you need to be careful that you don’t overwrite your Windows setup if you want your own PC/laptop to dual boot Windows & Linux. Installation instructions are here https://ubuntu.com/tutorials/install-ubuntu-desktop#1-overview.
Alternatively you can install Ubuntu to a USB stick and boot from that. Instructions here https://ubuntu.com/tutorials/try-ubuntu-before-you-install#1-getting-started.
We’ll pick up some Linux/Ubuntu skills along the way.
Accessing GitLab
Howto - http://www.ysjcs.net/linux_ssh_git.php
In terminal:
sudo apt-get -y install xclip
ssh-keygen -t rsa -N "" -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub | xclip -sel clip
Log into gitlab then click on the icon at the top right of the page, choose Settings and then SSH keys from the menu on the left.
Click in the Key box and press Ctrl+V (paste) then click Add key.
You should now be able to use git without entering a password. If a git command asks you for a password something has gone wrong with this key setup, so get in touch.
Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code (VSC) is an text based code editor. It is available for Windows, Linux and Mac from https://code.visualstudio.com/.
VSC has many extensions available for it, making it usable as an editor for most programming languages, scripting and most other things.
We’ll be using the extensions listed below
- C/C++ v1.6.0
- GitLens v11.6.0
- Code Runner v0.11.6
You might find the extensions below useful
- Bracket Pair Colourizer v1.0.61
- PlantUML v2.15.1
- Prettier - Code Formatter v.9.0.0
NB These are the version numbers I have installed. There may be newer versions.
Installing Extensions
When you have VSC open click on the Extensions button in the icon bar down the left hand side of the screen.

This will open up the Extensions side bar.
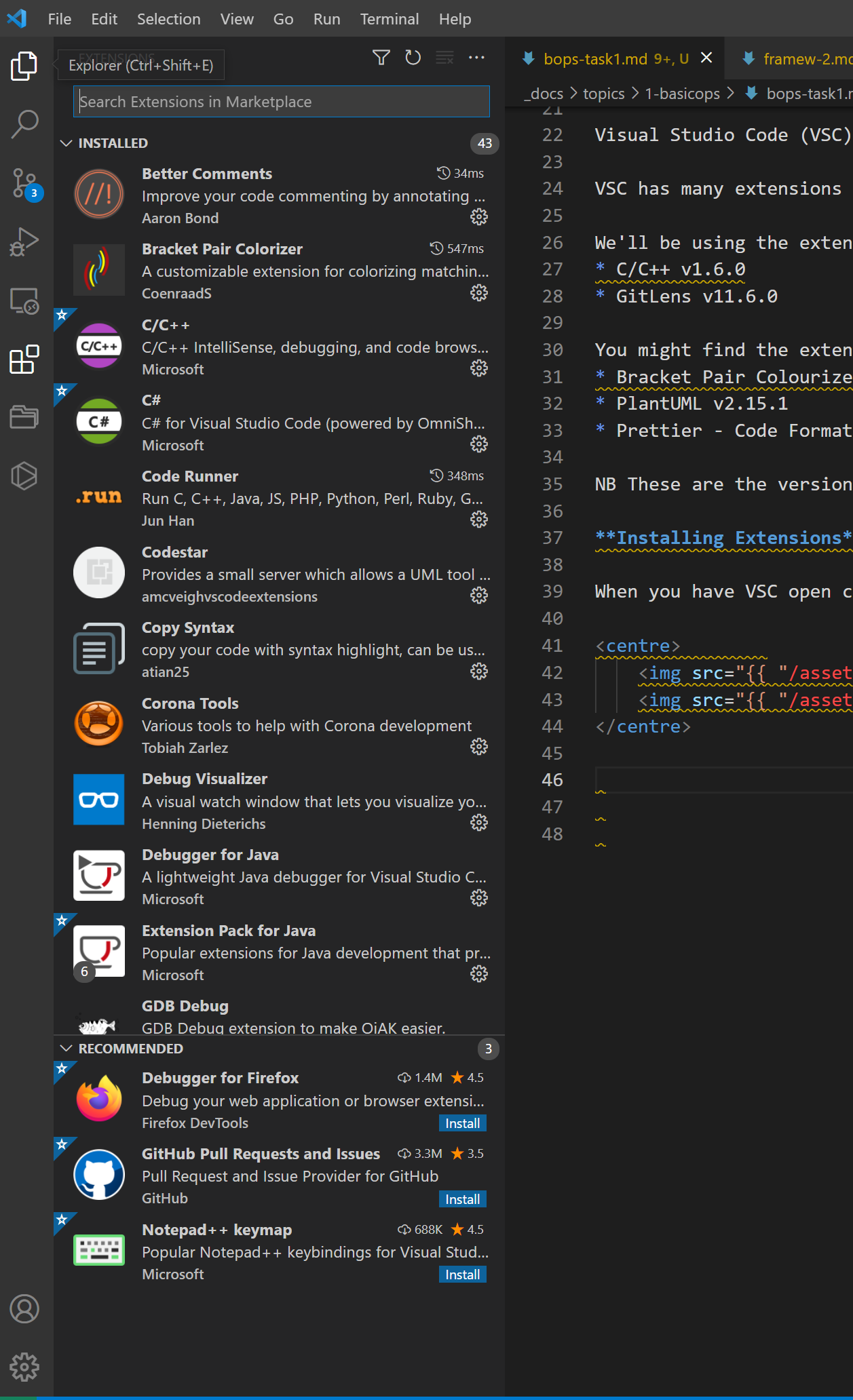
Type the name of the extension you want to install in the text box at the top of the Extension Bar and click the blue install button for the extension.
GitLens
If you’ve installed the GitLens extension correctly there should be an icon in the bar that looks like this.

Click on the button to open the Source Control sidebar.
Click on the Clone Repository button and enter the URL https://git.ysjcs.net:8888/a.guest/c001hello.git in the window that pops up.
Create a new folder to clone the repository to and select it.
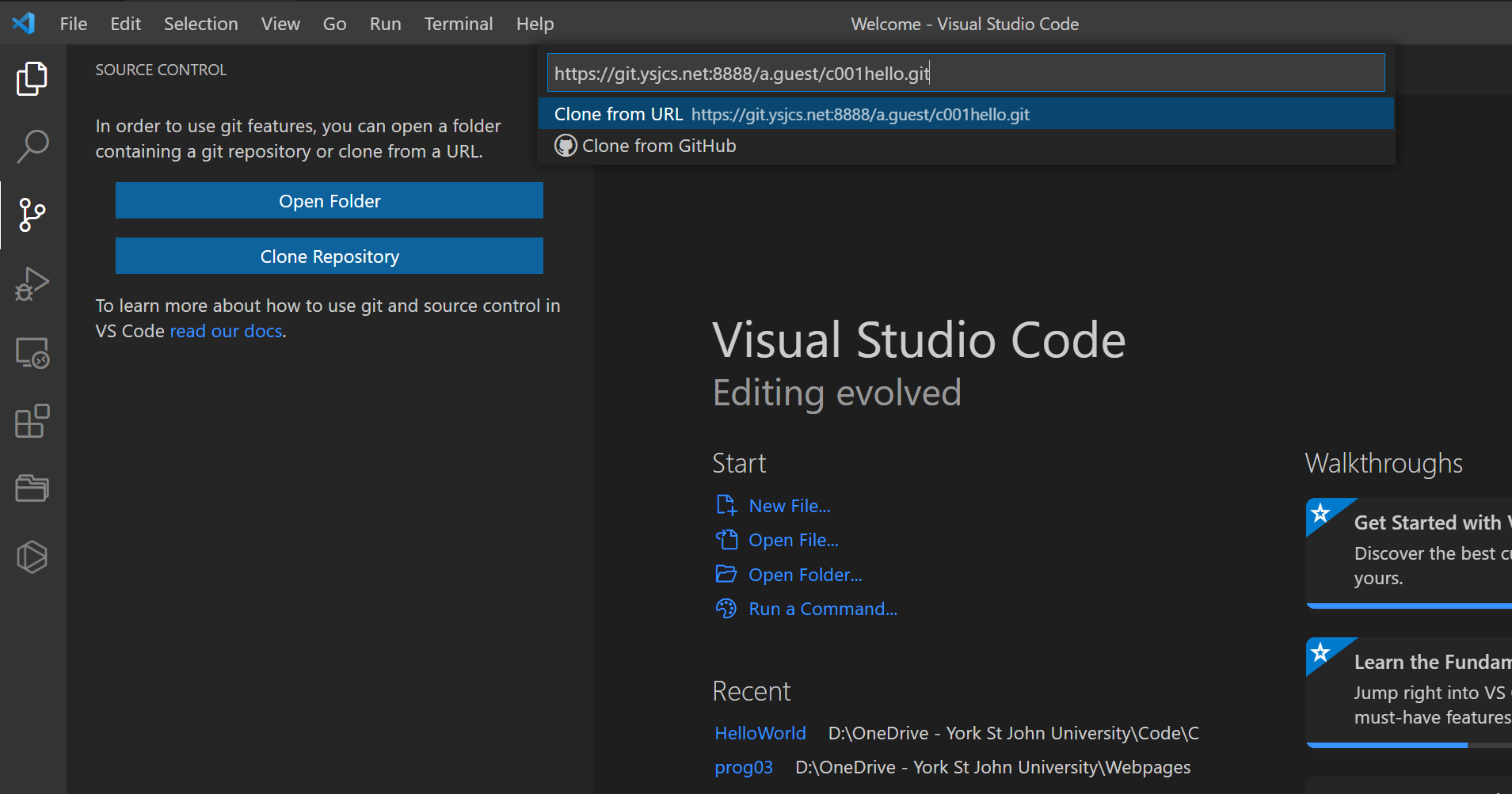
Click the Open button.
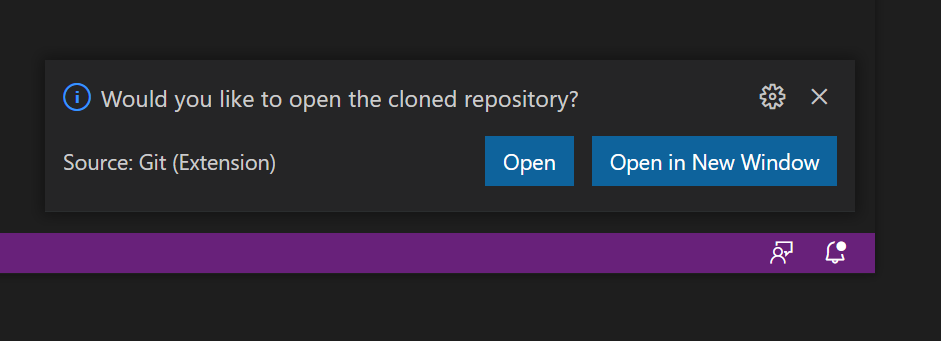
You should now have a copy of the Hello World c program.
If the terminal window isn’t open at the bottom of the VSC window, open it from the menu View, Terminal.
To run a C program we first have to compile it. Click on the terminal window and enter “gcc main.c -o helloworld”. We’ll discuss how this works later, but for the time being it triggers the Gnu C Compiler (gcc) to compile the c file main.c to create an executable file named helloworld.
To execute the program enter ”./helloworld”. The “./” tells the system the file is in the current folder.